To start our blog series about the procure-to-pay process, the first focus will be on purchase requisition in SAP. Creating a SAP purchase requisition and placing an order as the first steps of the procurement process can be optimized at large – comparing a classical purchase requisition with the SAP purchase requisition shows the benefits of digitalization.
Let’s first recall the entire procurement process in its typical form as an overview:
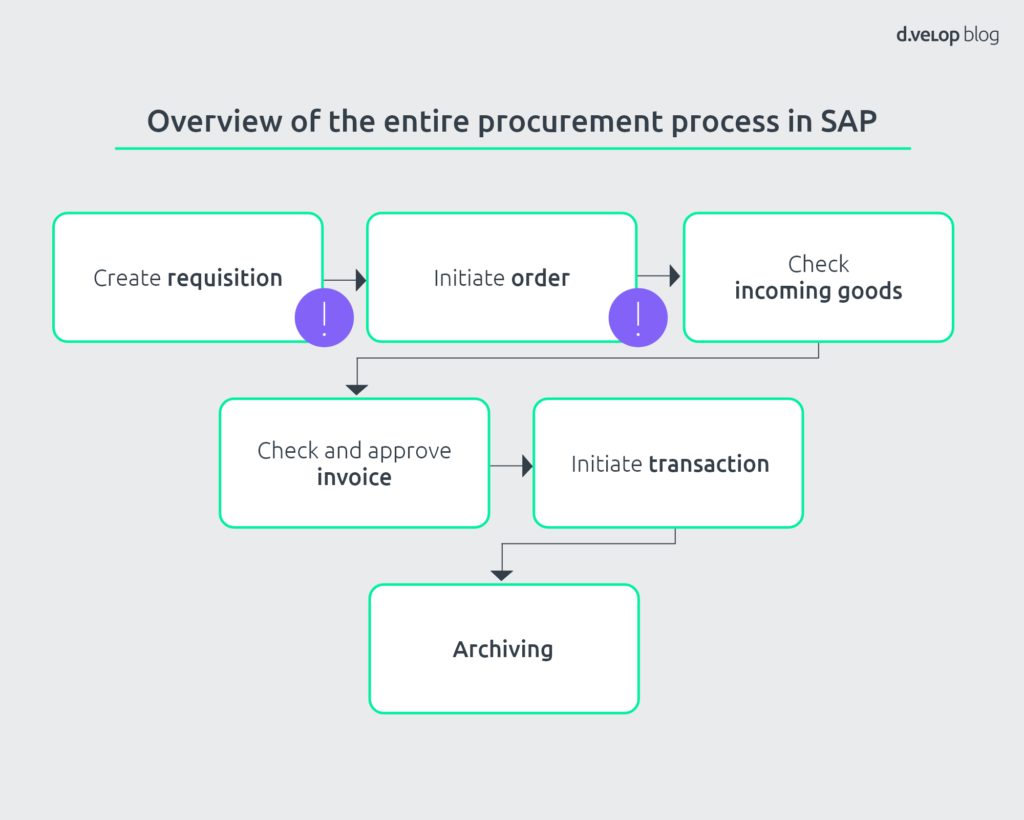
In focus: the SAP purchase requisition and the resulting purchase order
A purchaser faces the following “nerve-racking” questions every day:
- Is purchase requisition available for the required resource?
- Were the right goods selected for the purchase order?
- Which employee may review the purchase requisition?
- Which employee may approve the purchase requisition?
- Can I still edit the purchase requisition in the SAP system?
All these questions become obsolete when the process is automated. Why? Let’s start by taking a detailed look at how the SAP purchase requisition process is consistently digitized, and therefore simplified, by additional d.velop solutions.
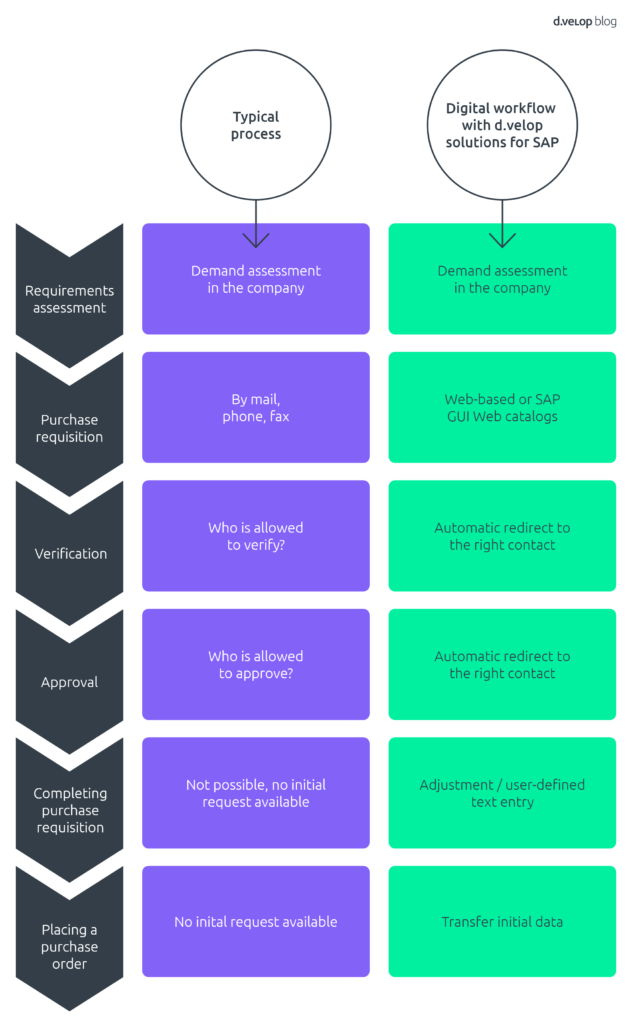
Requirements assessment
The input and trigger of the purchase-to-pay process is that a requirements assessment is performed.
In most cases, it proceeds as follows: Employees in different departments place orders via fax, e-mail or telephone, or casually tell their colleagues in purchasing or specialized departments on short notice. This initiates a time-intensive process. Colleagues must determine in advance whether quotations for these items are available, which suppliers they can order them from and whether the employee is permitted to order the items based on his or her authorizations and position. This results in a great deal of coordination and communication within the department.
In the automated process, the purchase requisition is triggered in the SAP system or per WEB GUI. By logging into the SAP system or using the WEB GUI, various predefined user roles are activated. This provides the employee with access to a web catalog of suppliers, which prevents errors in the procurement request. Plus, the cost center is automatically selected based on the selected supplier and then added to the procurement request. The systematic selection of suppliers further curtails the maverick buying effect. Additionally, centrally negotiated purchasing conditions are used and the correct supplier is usually always selected.
Verification of contents
The next step, verification of the procurement requisition, often lacks transparency when it comes to the responsibility for checking the purchase requisition for accuracy and completeness. This leads to an inordinate amount of coordination, not to mention the risk of false verification. This relative risk can lead to nonobservance of critical raw materials requirements, for example. Incorrect quantities or insufficient quality of such materials could lead to production gaps or increased associated costs as a result.
Since the automated process has a defined workflow, the procurement request is automatically forwarded to the responsible verifier. This ensures that company guidelines are met and the right items are ordered at all times. The correct quantity and quality is also ensured, and you can ensure that the items are available at the right time and place and also at the “right” prices. Automation ensures that the process is cost-efficient, without any interference or need for coordination. The procurement requisitions can also be conveniently checked from mobile devices without SAP access.
Approval process
The approval process often takes a significant amount of time and you usually need to request approval from numerous colleagues. For instance, investment requests typically require approval from controlling or management while raw materials need to be approved by the purchasing manager. Yet, when it comes to auxiliary and business materials, the direct supervisor usually has to grant approval. Non-automated procurement requests are often delayed when it is unclear who is responsible, and also when management is not on hand or has to deal with a high workload.
Accordingly, the benefit of an automated purchase requisition is definitely how much time is saved. After specifying which individuals are authorized to perform approval in the SAP system, procurement requests are forwarded to the responsible person according to the value limit or type of investment. The benefits are obvious: Any ambiguity is eliminated from the get-go, the process is made more transparent and it is ensured that approvals are processed much more quickly. The workload generated by follow-up questions – either in person, by telephone or e-mail – decreases dramatically.
Completing a purchase requisition
In a non-automated procure-to-pay process, the initial request cannot be modified in this process step, if necessary. This is caused by the lack of a procurement system in the system. Normally, the request exists in written form. A written document, however, makes it impossible to continually update information for various individuals and also is required to be printed out again by the department—often without knowing if the information is current—and delivered personally.
By contrast, the automated process makes it possible to modify purchase requisitions throughout the entire process chain and to add important information by entering supplemental text. Here as well, individual steps are made possible without any major need for coordination.
Placing a purchase order
Finally, a non-automated SAP purchase requisition requires you to manually capture the purchase order in the system. This means that the buyer has to manually enter the creditor, cost center, items, cost per piece, delivery date and delivery location before placing the purchase order. This involves a high amount of manual labor: In combination with the countless number of possible entries, processing is then vulnerable to error.
In the automated process, these sources of error are reduced to a minimum since the initial record is used for the purchase requisition. The SAP purchase requisition then cycles through the respective process steps. As a result, the purchase requisition undergoes continuous review, subsequently serving as a basis for the purchase order. By using the purchase requisition, the buyer can use the initial data and place the purchase order with the click of a mouse. Accordingly, sources of error are reduced and the purchase order is quickly and correctly entered in the system.
What can we take away from this? What are the benefits of the automated subprocess for purchase requisitions/ordering in SAP?
Overview of the benefits of a digital SAP purchase requisition
- Work efficiently without switching media
- Automatic gathering of purchase order data
- High level of process automation through direct pre-recording
- Processing and merging of accompanying documents
- Comprehensive reporting
- Involvement of the process owners without SAP access
- Clear guidelines and allocation of responsibilities and authorizations
In the next blog entry of our series, we will take a closer look at the step for incoming goods in SAP, followed by an analysis of SAP invoice verification and SAP archiving.

