We are experiencing a changing world of work. Work processes are being digitalised and streamlined, made more location-independent and more sustainable. We are seeing departments going completely digital and collaborating virtually. And we are seeing how easy it is to automate routine tasks and organise them without media discontinuity using suitable software. And yet there are still some media disruptions.
Bulky processes, such as contract amendments and signatures, which are usually handled via various media such as telephone, email and post, are sometimes riddled with security gaps and are also very time-consuming. In this blog article, you can find out how to digitalise processes holistically and thus design them without media discontinuity.
Media disruption: A definition
Media disruption is understood to mean a change of medium or channel in the transmission of information within the transmission chain. For example, whenever data that has been digitally captured cannot be continuously processed for further work and business processes (physical media disruption), or when switching between digital channels or tools within the process (virtual media disruption).
If overall processes, e.g. the processing of a document, are successful without changing the medium or channel in the process, we speak of a process without media disruption.
In which cases can media disruptions occur?
The reasons for and areas in which physical and virtual media disruptions occur can be very different. In general, we have identified the following areas:
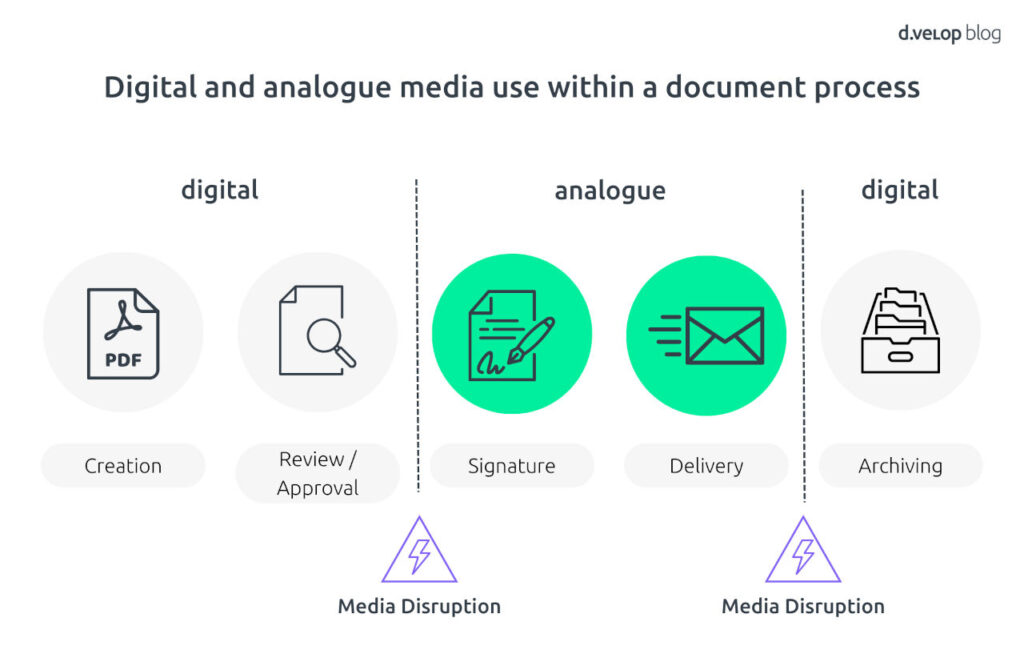
Digital and analogue media use within a process
If information is transferred from analogue to digital media — and vice versa — this does not occur without media discontinuity. A classic example of this is the digital creation and approval of a document that is printed out for signature and postal delivery, only to be scanned and archived again on the recipient’s side.
Use of different, incompatible software applications
If different software tools are used during a process that are incompatible or cannot communicate with each other, manual file transfers are required and a media break occurs. Example: An employment contract is created in a digital word-processing programme, then uploaded and signed in electronic signature software, downloaded again and delivered digitally via upload to another tool. The parallel use of incompatible tools during a document process can occur both within organisations — i.e. between departments or colleagues — and across organisational boundaries.
B2B: Data transfer between organisations
Whether offers, contracts, information letters or project plans: documents are exchanged and managed across organisations on a daily basis. However, the status quo of processing still varies from organisation to organisation. While some already work completely digitally, other organisations still have paper-based processes. One example is the exchange of data between suppliers and companies, which often still requires manual adjustments and therefore does not take place without media discontinuity if different process standards exist.
B2C: Data transmission between organisations and private individuals
Whether for payroll accounting or communication with insured people, for example, documents must find their way from organisations to private individuals and back again if necessary. If an organisation creates a payslip digitally, for example, then prints it out for dispatch and sends it by post to an employee, who in turn scans it in and archives it in a digital folder. There are multiple media disruptions. Especially when documents contain sensitive, personal data, their protection should be a top priority and guaranteed by a process free of media discontinuities.
Why organisations should work without media disruptions
The more media breaks a process contains, the more disadvantages it has. We have listed the possible disadvantages below:
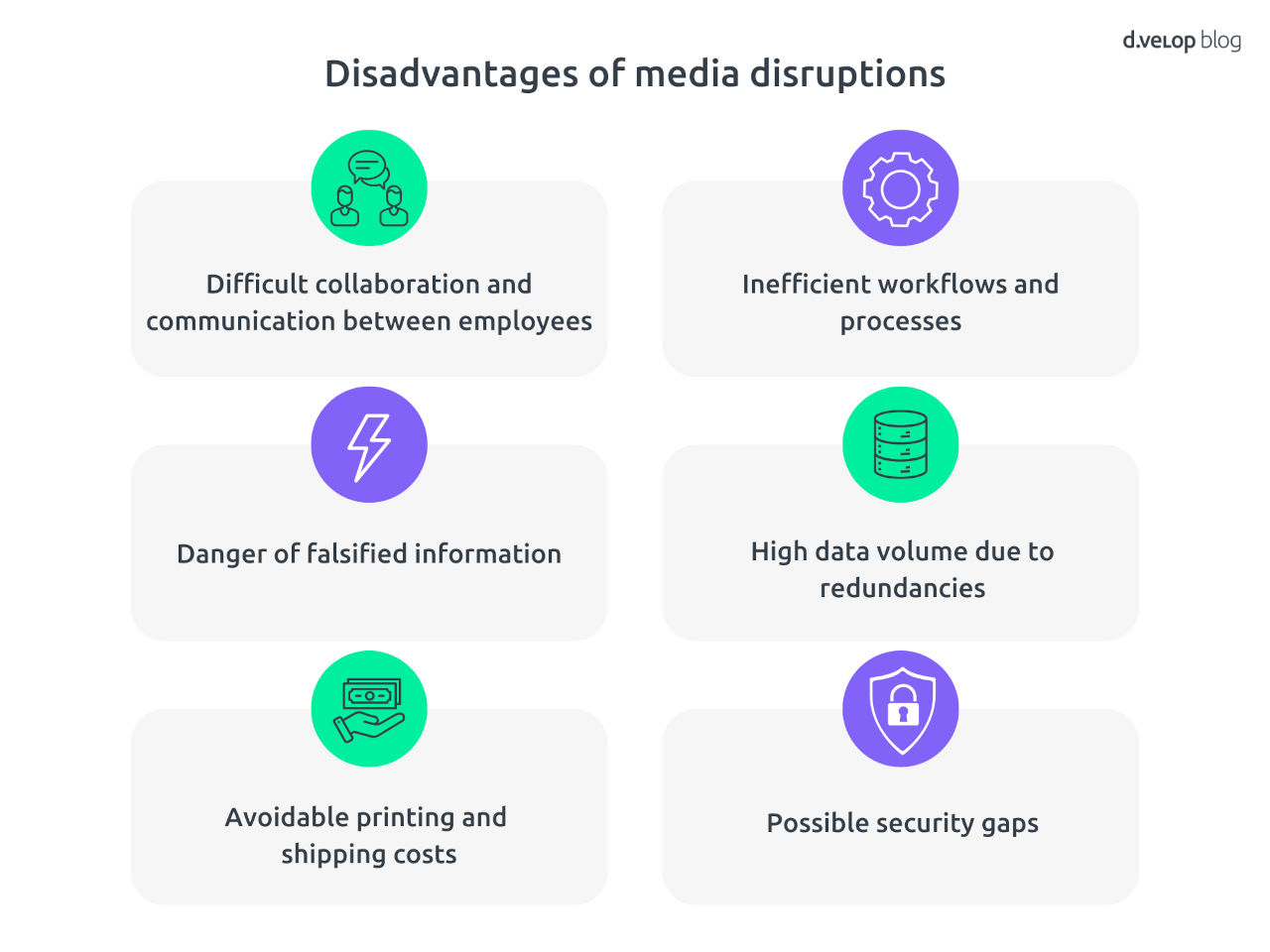
- Difficult collaboration & communication: Media disruptions can make collaboration and communication between employees considerably more difficult, as information cannot be exchanged seamlessly.
- Inefficient & redundant processes: Media disruptions result in inefficient workflows as information has to be transferred manually and processed multiple times because it is not available in a centralised medium.
- Risk of information falsification & increased susceptibility to errors: When transferring information between different media, there is a risk of data being falsified or misinterpreted, which can lead to errors and misunderstandings.
- High data volume due to redundancies: Media disruptions often lead to redundant data and tasks, as information is stored and processed multiple times, which puts a strain on servers and networks. This also slows down processes and complicates them.
- Avoidable printing & shipping costs: The use of paper and physical documents causes avoidable costs for printing and shipping.
- Potential security gaps: Different media can have different security standards, leading to potential security gaps. Manual transmission increases the likelihood that information can be falsified, not transmitted or viewed by unauthorised third parties. This is particularly critical in areas where data protection is a major issue.
- Delayed decision-making: Media disruptions can mean that it takes longer for all relevant information to be available, leading to delays in important decisions.
- Lack of transparency of process steps: Media disruptions can lead to tasks not being documented satisfactorily, which makes tracking and feedback more difficult. Tracking across different media and perhaps even organisational boundaries, such as emails, printed, hand-signed documents, scanning and filing can be very time-consuming.
Collaborate without media disruption and simplify processes with digital solutions
Due to the negative aspects of media disruptions, one thing is clear: they must be avoided as far as possible. Digital processes can minimise many of the disadvantages of media disruptions. This not only refers to internal organisational processes, but also processes that extend beyond the boundaries of the organisation. Some examples are customers, clients, patients, insured people or employees. The aim must be to provide information digitally and to process feedback digitally.
Many employees are already very digitally oriented in their private lives and, for example, want simple digital handling of personnel documents without the time-consuming sorting, signing and archiving of documents. Digital mail delivery, for example, is one solution. Documents can be delivered easily, securely and digitally and are archived directly in the user’s private, digital mailbox.
For the dispatch of documents, this means
- No paper
- No great expenditure of time
- No bulky processes
- No investment in envelopes, machines or similar.
- No security gaps
- Document delivery without media disruption
Digitise document processes holistically
In the modern working world, documents are currently scattered across different devices, locations, and apps. Organisations, but also private individuals, must always be able to access and work with documents from anywhere. Be it for exchanging, editing, signing, or sending.
The d.velop platform can map all these document processes around the document lifecycle without media discontinuity. Be it the digitalisation of classic end-to-end processes or special, more complex projects.
Media-break-free signature circulation of documents with d.velop sign
In most cases, we already create documents such as an employment contract completely digitally, e.g. with text editors such as Microsoft Word. With d.velop sign, the employment contract can now also be signed digitally and in a legally secure manner. For this purpose, the employment contract is loaded into d.velop sign and a new digital signature circulation is started. The initiator of the signature circulation can invite several internal or external people (even without an account) to sign. He then selects a signature level (simple, advanced, qualified) and, if required, defines further settings, such as automatic reminders or a specific signature sequence. Once the signature cycle has started, the people identify themselves and sign the document digitally and without media discontinuity. After a successful signature, the employment contract can be digitally archived and then delivered.
Archiving and managing documents without media disruption with d.velop documents
Managing personnel files can often be time-consuming and confusing. These files must be stored and archived centrally, and access to these documents is strictly regulated. A digital personnel file can considerably simplify, centralise and digitise this process. All relevant personnel documents, such as employment contracts, application documents or payslips, are stored in a document management system without media discontinuity.
Why opt for a digital personnel file?
Digital personnel files increase efficiency, provide a clear and well-structured HR document management system, and simplify day-to-day work. Employees also benefit — for instance, when holiday requests are approved at short notice or when certificates can be issued quickly. In times of remote work, HR staff working from home are no longer tied to paper folders. Thanks to the digital personnel file, they can access and manage employee data easily and securely from anywhere.
Key Features of a Digital Personnel File
- Automated processes:
- Workflow-supported automation of all HR-related processes.
- Tasks and process steps are never overlooked, thanks to automatic reminders and task management.
- Existing filing structures can be mirrored 1:1 within the digital file plan.
- Legally compliant archiving:
- All retention periods, data protection regulations, archiving obligations, and deletion deadlines in accordance with GoBD are automatically and strictly observed.
- All documents — from employment contracts to sick notes — are archived centrally, space-efficiently, and without media disruptions.
- Easy search and retrieval:
- Tailored search functions allow you to find any file details within seconds, even years later — saving valuable time.
- Misfiled documents are quickly identified and corrected.
Seamless Document Delivery with d.velop postbox
Once both parties have signed the employment contract and the organisation has securely archived the document in its DMS, it should then be delivered safely to the future employee.
A seamless and efficient way to do this is via delivery to a digital mailbox, which remains in the employee’s personal ownership for life. Organisations can send the employment contract directly from their DMS or document creation software using d.velop postbox, fully compliant with the GDPR and with just one click. Employees then have all their personal documents stored digitally in one place and can easily share them with third parties — for example, their tax advisor or landlord.
Other HR documents, such as payslips or income tax statements, can also be delivered securely and without media disruptions to the employee’s private digital mailbox in the same way.
Digital payslip delivery
The aim of this white paper is to present the optimal solution for your digital payroll delivery and guide you through the steps to implement this in your company.
With a powerful document management system such as d.velop documents, the handling of (HR) processes without media discontinuity is accelerated, transparent processes are ensured and the ability to provide information is improved. Supplemented by digital signature software and the digital delivery of documents, the result is a holistically digital document process without media discontinuity, which also protects the environment.
Conclusion: Holistic digitalisation promotes efficient, secure and seamless processes
Digitalisation is a long-established trend that is already being implemented in most organisations. Efficiency and automation are also playing an increasingly important role for organisations. Tools such as d.velop sign, d.velop postbox and d.velop documents combine these topics and enable collaboration without media discontinuity — both within organisations and across organisational boundaries. They not only reduce the complexity of processes, but also increase their security and efficiency.
Frequently asked questions about media breaks
What is a media disruption?
A media discontinuity occurs when information is transferred from one system to another and there is a change from one medium to another. This can be the case, for example, if data that has been digitally recorded once cannot be continuously processed for further work and business processes.
What is the significance of a media disruption?
A media disruption can lead to increased susceptibility to errors, longer processing times and higher costs. It is therefore essential to avoid media breaks as far as possible.
How can media disruptions be avoided?
One way to avoid media disruptions is to digitalise processes holistically and minimise the manual input of information. Implementing interfaces between different systems can also help to avoid media disruptions and enable seamless data exchange.
What are examples of media discontinuities?
One example of a media discontinuity is the manual input of data from a paper document into an electronic system. If an invoice is received by the company as a PDF document but is printed out for further processing, the medium changes from a digital PDF file to paper, another example of a media discontinuity.