Invoice checking, approval and release, a critical process that every company undertakes. Nothing new so far. But why is it crucial to digitise invoice approval – especially if you use SAP? Today’s blog article explains: Find out how digital SAP invoice approval not only increases efficiency in your company and saves costs, but also contributes to higher compliance and a more sustainable way of working. Have fun!
Definition of invoice release in SAP
SAP invoice approval refers to the process by which invoices are reviewed, approved and released for payment within a company, using SAP software as a tool for this process.
SAP invoice approval: A sub-step of a large process
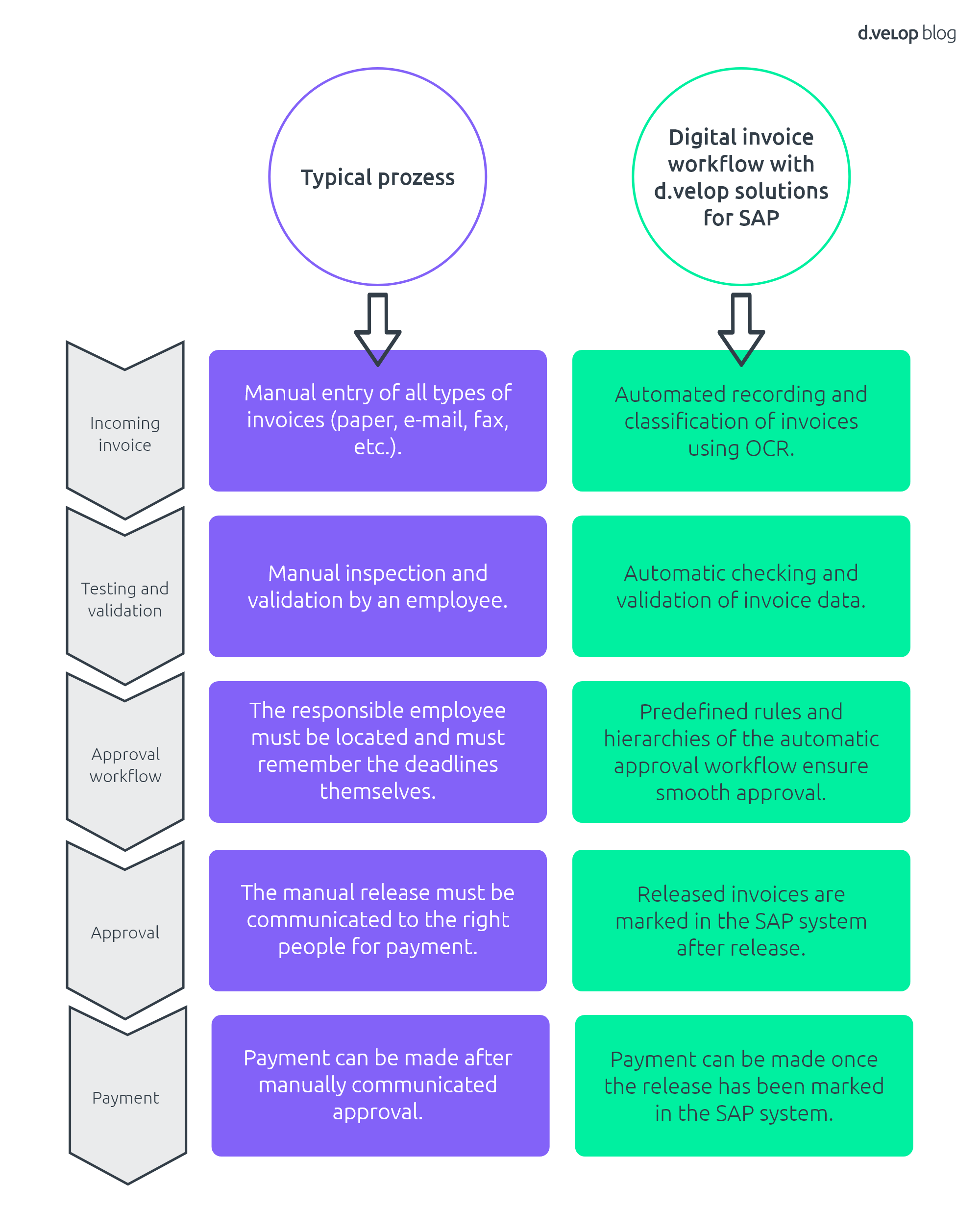
The release of invoices in SAP can be classified into a process chain in the Finance & Controlling department. Parts of this process include invoice receipt, verification and validation, approval workflow, release and payment.
- Invoice receipt: Suppliers send invoices to the company through various channels for services provided or goods delivered.
- Checking and validation: The invoices are entered into the SAP system, where they are checked for accuracy and completeness. This can be done automatically or manually by employees.
- Approval workflow: After checking, the invoices must be approved by the relevant responsible persons before they can be forwarded for payment. Here, predefined rules and hierarchies can be set to ensure that the right people grant approval.
- Release: The approved invoices are marked in the SAP system and released for payment.
- Payment: After approval, the invoices are paid.
We will take a closer look at steps 3 and 4 in particular.
Creation of workflow rules for automated invoice approval in SAP
Let’s start with creating defined workflow rules and hierarchies. To illustrate this, let’s go through a possible process step by step:
- Assign Approval Request: First, the specific rules for invoice approval need to be set. Determine who should receive the approval request based on various criteria such as: invoice amount, cost centre, supplier, or other user-defined factors.
- Configuration in the SAP system: The defined rules must be configured in the SAP system. This can be done in the invoice approval or workflow management settings.
- Define user roles in the approval process: User roles must be defined according to the workflow rules. This means that certain users or groups take on certain tasks in the approval process.
- Define workflow trigger criteria & steps: The workflow is triggered when a new invoice is entered into the SAP system. This can happen automatically when invoice data is imported or transferred from other systems. The workflow consists of several steps that determine what to do at each stage of the approval process. This could be the automatic checking of invoice data for accuracy and completeness, followed by forwarding to the appropriate approval authorities.
- Set up automatic messages: If necessary, notifications can be sent to users to inform them of pending tasks. Escalation rules can also be defined to ensure tasks are completed on time.
- Creation of reports: The workflow status and approval history are recorded in the SAP system. This makes it possible to track progress and generate reports on the invoice approval process.
- Payment release & integration into accounting: After successful approval, the approved invoices are released for payment and integrated into accounting.
Note: It is important that the exact configuration and integration of workflow rules in SAP depends on the specific requirements and individual settings of the company. Therefore, it may be necessary to seek the support of SAP experts or consultants.
From theory to practice: This is how the approval workflow works in many companies
After the invoice has been digitally recorded and checked for complete and correct data, the approval workflow starts based on predefined rules and criteria.
A correctly defined approval workflow determines which employee approves the received invoice for payment. Approval requests are automatically sent to the appropriate people or departments – in most companies, who receives which invoice is determined based on the invoice amount and/or cost centre.
To illustrate this: All invoices from supplier XMZ Ltd with an invoice amount of €5,000 or more must be approved by Mr Black, Head of Purchasing. Ms. Jones releases everything below the amount. If these two are absent, the invoices are automatically sent to Ms. Little for approval.
The notifications contain information about the invoice and a link or interface for approval. The authorised people can approve the invoice directly from the notification. This can be done with the d.velop solution in SAP, for example via a web client, from the SAP GUI or SAP Fiori interface.
If the invoice is not approved within a certain time period, the system can automatically send escalation notifications or escalate the matter to the next level of authorisation. After successful approval, the invoice is released for payment and transferred to the financial system.
Finally, a plea for the digitalisation of SAP invoice approval
The release of an invoice is an essential step in the overall process of invoice processing in SAP. At the same time, this step can be prone to delays. Sometimes responsibilities or representation rules for approving invoices are not clearly defined for all employees. This results in a lot of effort in terms of agreements. During manual checking and approval, errors can occur, which lead to further coordination effort or, in the worst case, incorrect bookings. In addition, external and internal compliance requirements play a major role in SAP invoice approval. These must be considered when processed manually. Last but not least, the amount of paperwork also plays a role, which is significantly higher in the manual process.
In summary, digital SAP invoice approval improves throughput times by eliminating media disruptions. It offers transparency for everyone involved, reduces the error rate during checking and approval. Whilst compliance requirements are met through predefined rules and paper consumption and costs are significantly reduced.
