In recent years, the flow of digital data has seen a remarkable surge. Our online presence has expanded beyond private matters, as businesses embrace digitization, leading to an abundance of personal digital data. To address this, the European Union implemented the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in 2018. Learn more about GDPR, its implications for SAP compliance, and how it could affect your company.
What is SAP Compliance?
In the context of SAP, compliance means strictly adhering to legal regulations and internal company guidelines. Achieving compliance involves conducting a precise and clear analysis of the internal processes within SAP. When referring to legal regulations, the focus primarily lies on the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), also known as the DSGVO.
DSGVO as a basis for SAP compliance
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a European Union regulation that oversees the processing of personal data. Its primary objective is to ensure robust protection for this data and to promote the unrestricted movement of data within the European single market.
In accordance with Art. 4 No. 1 of the GDPR, “… personal data refers to any information that relates to an identified or identifiable natural person …”. An identifiable person is someone who can be recognized using details like their name, location data, online identifier, or specific characteristics reflecting their physical, physiological, genetic, mental, economic, cultural, or social identity. It’s essential to note that data related to companies or legal entities, like limited liability companies, is not considered personal data unless it contains information pertaining to individuals.
The GDPR primarily focuses on specific regulations regarding the deletion, blocking, and storage of personal data. Notably, it outlines nine fundamental principles that govern the storage of such data.
Principles for the storage of personal data
1. Legality
In essence, this implies that every handling of personal data must be carried out in strict compliance with the lawful provisions outlined in the GDPR.
2. In good faith
This principle is assessed on a case-by-case basis. In general, it signifies that data processing should be conducted in a truthful and respectable manner.
3. Transparency
Under Art. 15 et seq. of the GDPR, data subjects are granted the right to exercise informational self-determination. This allows them to request confirmation from the data controller regarding the processing of their personal data and gain insights into the specific processing purposes, intended data storage duration, and other relevant details.
4. Earmarking
Personal data should only be collected for transparent and lawful purposes.
5. Data Minimization
The collection of data should be restricted to the intended purpose and necessary processing, taking into account the volume of data involved.
6. Correctness
Personal data must be factually accurate and, when required, kept up to date. In case of any erroneous data, appropriate measures should be promptly taken to rectify the issue.
7. Memory limitation
In accordance with the storage limitation principle, personal data should be retained in a way that allows for identifying data subjects only for the duration necessary to fulfill the purposes for which the data were processed.
8. Integrity and Confidentiality
Personal data should be processed and stored with the utmost security, preventing unauthorized access, unlawful processing, accidental loss, destruction, or damage to the data.
9. Accountability
The data controller holds the responsibility for adhering to data protection principles. To comply with the GDPR, the controller must be able to demonstrate their compliance. This is achieved by preparing relevant documentation to meet data protection requirements, which may include a directory of processing activities.
High Fines for Violations
The GDPR regulations can appear extensive and initially complex, yet the consequences of non-compliance are significant. According to Art. 83 (5) (a) of the GDPR, violations can lead to fines of up to €20 million or, for companies, up to 4% of their total worldwide annual turnover from the preceding fiscal year—whichever amount is higher. Given the high stakes involved, dedicating time and effort to SAP compliance is undeniably worthwhile.
Managing SAP Compliance with SAP’s ILM Module
Originally designed to manage the lifecycle of quality management information, the SAP module ILM (Information Lifecycle Management) now plays a crucial role in GDPR implementation. This module facilitates data archiving, retention management, and data flow control. By employing deletion and blocking rules, personal data can be appropriately managed, including blocking, archiving, and deletion as needed. The goal is to optimize data flows, streamline IT system expenses, and mitigate legal compliance risks associated with specific data collection processes.
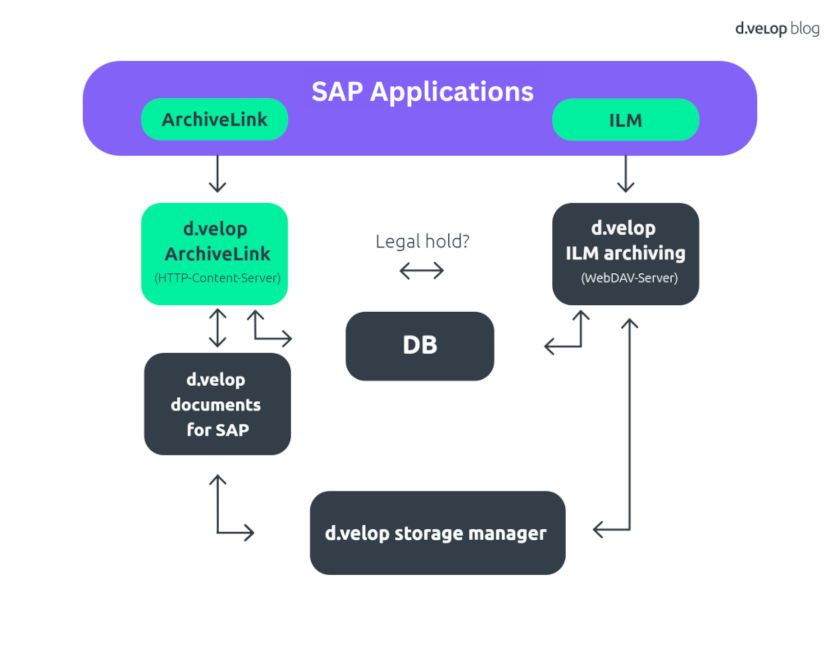
The d.velop SAP Compliance Solution
The ILM module of SAP enables the archiving of data through an ILM-capable repository like d.velop ilm archiving for SAP Solutions. This includes personal document data, optionally associated ArchiveLink links, and their corresponding retention and deletion periods. The data is then transferred to the d.velop storage manager, where it is stored. Following the defined retention and deletion periods, data is automatically deleted unless SAP ILM imposes a legal hold on it.
The integration of d.velop ArchiveLink for SAP Solutions and d.velop ILM Archiving for SAP Solutions ensures that ArchiveLink documents are removed prior to the expiration of the ILM retention and deletion periods.
In practice: When considering personal data, our thoughts often gravitate towards information related to human resources within companies. However, personal data is also prevalent in procurement and sales processes. As previously mentioned, the GDPR emphasizes the storage limitation principle, requiring the deletion of personal data once it has served its purpose.
Consider a scenario where a company receives an incoming order containing personal data. The company processes the order, fulfills the shipment of goods, and subsequently issues an invoice. Once the customer completes the payment for the goods, the entire process concludes. Consequently, in compliance with the GDPR, personal data should be promptly deleted.
During the SAP ILM module implementation, collaboration with an ILM consulting partner is essential to devise a deletion concept aligned with GDPR guidelines. However, the varying legal circumstances in different countries can give rise to deletion conflicts. While the GDPR mandates information deletion, state laws in Germany, such as the German Commercial Code (HGB) or German Civil Code (BGB), impose specific retention obligations, leading to potential conflicts between the two requirements.
The d.velop ILM archiving module plays a pivotal role in aligning the deletion concepts specified in your SAP ILM rules with country-specific framework parameters. This ensures that archived documents and records adhere to the defined rules. In instances where deletion is not permissible due to fixed retention periods or legal holds, the relevant documents are secured and accessible only to authorized personnel. Once the retention period concludes, the documents are automatically deleted, streamlining the deletion process with utmost compliance.

Your SAP Compliance Management Strategy
To ensure robust SAP Compliance Management, both the ArchiveLink and ILM interfaces are essential. While the ArchiveLink interface handles classic document storage, our ILM interface, d.velop ILM archiving, directly processes and stores documents in the storage manager area. When specific documents require deletion, a manual verification with the classic SAP ILM module is performed. With our product, d.velop ILM archiving, we ensure the seamless implementation of rules defined in the ILM module through automated processes, enhancing compliance and efficiency.
Protect yourself from high penalties with SAP Compliance
While DSGVO-compliant archiving of personal data in SAP compliance might not be the most entertaining subject, it’s important to adhere to regulations ensuring compliance that can safeguard your organization against substantial fines.
Experience d.velop SAP solutions live
Book your individual software demo for the d.velop solution with just a few clicks. Let our experts show you the software live and ask your questions directly.
