Traditional production processes often reach their limits when it comes to flexibility, efficiency, and traceability. The digitalisation of production addresses these issues by replacing manual processes, paper-based documentation, and isolated systems. These changes can lead to errors, bottlenecks, and inefficient workflows. These challenges can be overcome through the digitisation of production.
What does digitalisation mean in production?
The term digitalisation in production refers to the improvement of traditional manufacturing processes. It uses digital technologies aimed at enhancing quality and efficiency.
What developments are revolutionising digitalisation in production?
From automation to the use of the Internet of Things (IoT) to leveraging Big Data, these innovations are revolutionising production processes. They also foster an innovative and efficient future for the industry. The advancing chapter of Industry 5.0 marks a crucial turning point in the manufacturing landscape. It elevates the digitalisation and connectivity of people, machines, and products to a new level. Additionally, automation and artificial intelligence play a central role in Industry 5.0. Automation is a significant aspect of the transformation of digitalisation in production. The use of advanced robotics systems and intelligent process controls enables increased efficiency and precision in manufacturing.
Artificial intelligence as a driver of digitalisation in production
It’s no longer a new insight that Artificial Intelligence (AI) will fundamentally change the working world. Developments in AI are rapid and will significantly influence the industry in the coming years. AI technologies revolutionise production processes. They also transform document management and enable predicting maintenance needs and adjusting manufacturing parameters in real-time. As a result, AI significantly contributes to increasing the flexibility of production facilities within the framework of digitalisation in production. Moreover, there is a clear trend towards intelligent process automation (IPA), which combines traditional robotic process automation (RPA) with AI, machine learning (ML), and natural language processing (NLP). This trend is gaining more importance in the future.
Digitalisation of Production: Networking Production Components through Smart Technologies
In addition, the interconnected world of smart devices on the Internet of Things (IoT) plays a crucial role in the transformation process. Through the integration of IoT technologies, machines, tools, and production facilities become interconnected and communicating units. IoT enables real-time monitoring and control, as well as comprehensive data capture. Big data analysis methods are applied to the resulting data masses to gain insights far beyond conventional analyses. Big data refers to large amounts of data that accumulate in great variety and at high speed. Analysing big data allows for process optimisation by identifying patterns. It also helps in making informed decisions. This data-driven approach not only supports efficiency improvements and the digitalisation of production. It also aids in the continuous improvement of production processes.
Cyber Risk Management in the Context of Current Threat Scenarios
With the constant increase in interconnected systems and data streams, cybersecurity is also becoming increasingly important.
The threat landscape in cyberspace is tense, dynamic, and diverse, making it higher than ever before.
BSI – Federal Office for Information Security
Given this, securing production facilities against cyberattacks becomes an essential challenge in the digitisation of production. To ensure the protection of sensitive production data and smooth operation of manufacturing processes, intelligent security concepts and technologies are required.
Document management gets even smarter, thanks to the latest AI technology
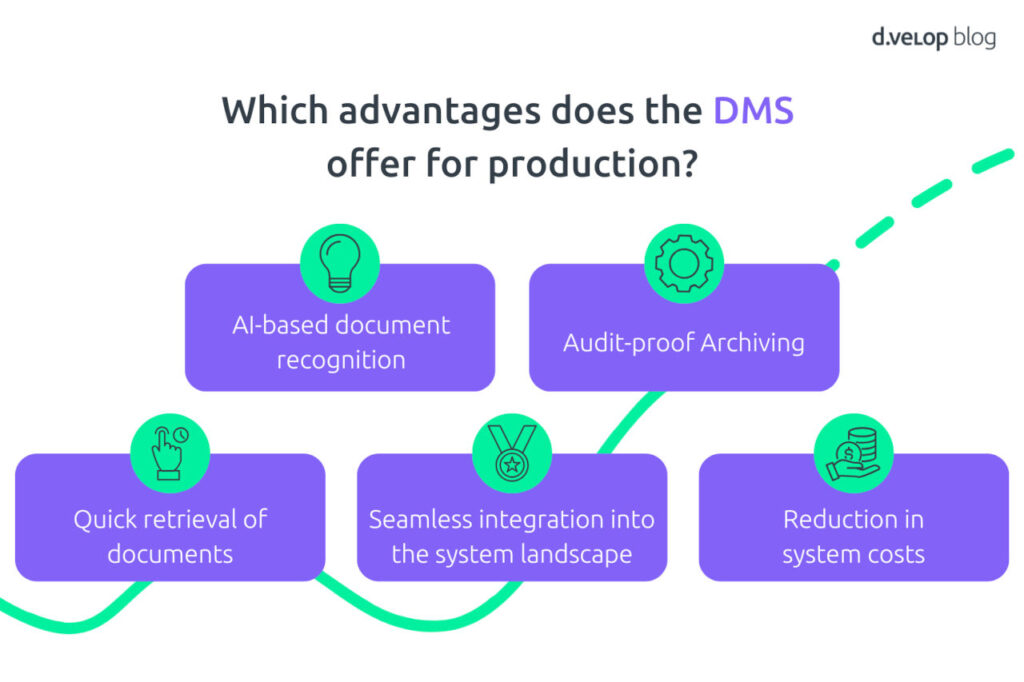
In recent months, alongside ChatGPT, numerous generative AI models have been released to help automate document and business processes in the digitalisation of production. Working with models based on natural language makes artificial intelligence accessible to everyone at a disruptive pace. An AI-powered Document Management System (DMS) enables automatic AI-driven document recognition and summarisation. It supports real-time chat functions for document inquiries or user interaction via voice. This system allows for automatic recognition, categorisation, and extraction of key information from large volumes of documents – all without manual intervention.
💻Book Software Demo
Experience the power of d.velop’s software with a personalised live demo, easily requested with just a few clicks. Watch as the software comes to life before your eyes and ask any questions you may have in real-time.
