The use of artificial intelligence is steadily increasing in German companies. According to Bitkom, 15 percent of companies are now actively using AI technologies, while more than two-thirds of surveyed businesses consider artificial intelligence to be the most important future technology. The types of AI technologies in use vary significantly – ranging from rule-based systems to deep learning methods and generative AI. This article introduces the different types and subfields of artificial intelligence to provide a deeper understanding of how they work, their applications, and their potential.
Strong AI vs. Weak AI
As early as 1955, former Stanford professor John McCarthy defined artificial intelligence as “the science and engineering of making intelligent machines”. Other definitions go even further, describing AI as “the ability of a system to exhibit intelligent behaviour comparable to that of a human being”.
It is the science and engineering of making intelligent machines, especially intelligent computer programs.
John McCarthy, former Stanford professor
AI approaches are often still divided into two main categories: Weak AI and Strong AI.
- Weak AI (Narrow AI): Weak AI refers to artificial intelligence designed to solve a specific problem. It can perform a particular task but cannot generalise its learned abilities or transfer them to other tasks.
- Strong AI (Artificial General Intelligence): Strong AI, often referred to as Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), is a theoretical form of AI that aims to achieve intelligence comparable to that of humans. Unlike weak AI, which is limited to specific tasks, strong AI can perform a wide range of functions and evolve independently over time.
Subfields of AI
The methods used in artificial intelligence are divided into various subfields, forming the foundation for AI applications in business. Below are some of the key subfields and methodologies:
- Knowledge Representation and Reasoning: This area of AI focuses on representing information about the world in a form that a computer system can use to solve complex problems.⁵ Early systems date back to the 1960s and are based on technologies such as semantic networks, ontologies, and mathematical logic.
- Expert Systems: Expert systems are computer programmes that mimic the decision-making abilities of a human expert. They are designed to solve complex problems by accessing a knowledge base. The first such systems emerged in the 1970s and are among the earliest successful forms of AI software.
- Machine Learning: Machine learning is the area of AI that enables computers to learn without being explicitly programmed. Unlike rule-based systems that follow predefined instructions, machine learning models learn to solve problems independently using training data. The model learns solely from examples and does not require manual programming.
- Deep Learning: Deep learning is a subfield of machine learning based on deep neural networks. These artificial neural networks simulate the basic functioning of the human brain and enable learning from large datasets.
- Generative AI: Generative AI refers to deep learning models capable of generating high-quality content such as text, images, and more. These models are typically trained on vast amounts of data, often sourced from the internet.
Applications of Artificial Intelligence
AI applications use artificial intelligence technologies to perform specific tasks. These can range from simple, repetitive activities to highly complex challenges. Below, we highlight three selected areas of AI application:¹
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Natural Language Processing enables applications to understand human language. NLP uses machine learning to process and interpret textual data. It is widely used in document-related tasks: for example, NLP can classify documents by identifying whether a file is an invoice or a delivery note. Furthermore, NLP can automatically extract specific information from invoices or other documents with high accuracy.
- Computer Vision: Computer Vision is a field of artificial intelligence that uses machine learning to process and interpret visual information. With the help of algorithms, computer vision systems can recognise objects, analyse patterns, and understand visual data. Applications range from facial recognition to image analysis in fields such as medicine, autonomous driving, and quality control in manufacturing.
- Robotics: Robotics is the branch of artificial intelligence concerned with the design, construction, and operation of robots. Robots are used in various applications, including manufacturing, healthcare, and space exploration. By integrating AI technologies, they enable advanced automation and the ability to perform a wide range of tasks across different industries.
The Impact of Generative AI Models
Since the release of ChatGPT in November 2022¹, the development of generative AI models has progressed at an extraordinary pace. These models are based on deep learning techniques and are capable of generating high-quality text, images, and other content.⁹
Large Language Models (LLMs) as the Core of Generative AI
The most widespread subcategory of generative AI models is known as Large Language Models (LLMs). These are generative AI systems specialised in producing textual content. One example is GPT-4, the language model that powers ChatGPT.
Generative AI models are typically built on foundational models – large-scale language models with billions of parameters trained on massive datasets, often sourced from the internet. These foundational models can already perform a variety of tasks, including summarisation, question answering, classification, and more. Moreover, foundational models can be adapted to specific use cases with only a small amount of training data. This process, known as fine-tuning, does not require training the model from scratch but instead adjusts only a subset of the parameters learned by the foundational model.
The use of generative AI in companies is growing rapidly. In a 2024 survey conducted by Salesforce, 61% of respondents stated that they were either already using generative AI in their daily work or planning to do so in the near future. Additionally, more than two-thirds of those surveyed said that generative AI would help them better address their customers’ needs.
Rising Adoption and Potential of Generative AI in Business
Generative AI offers a wide range of applications for businesses. For example, it can automatically summarise long texts or even entire meetings. Companies are also using generative language models to provide high-quality voice bots for customer support. In general, generative AI opens up entirely new possibilities for processing large volumes of unstructured data.
Strong vs. Weak AI – Where Do We Currently Stand?
After exploring the definitions of weak and strong AI, the question arises: how far have developments in these areas progressed? Researchers at Google DeepMind have proposed a model to assess this, outlining progress across five successive levels. This classification is illustrated in the following table.
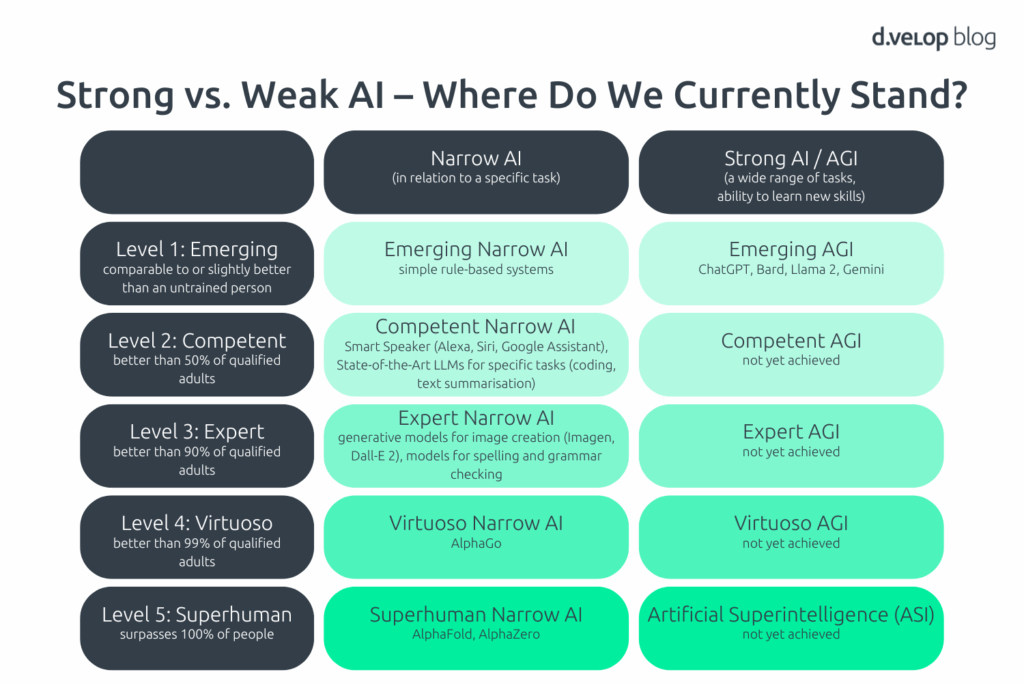
The researchers note that in the field of weak AI—that is, AI models designed for specific tasks—there are already systems that outperform 100% of humans in certain domains. One such example is AlphaFold, a specialised model developed by Google to predict protein structures based on amino acid sequences.
In contrast, the picture is different when it comes to strong AI. While early Large Language Models (such as ChatGPT, Bard, Llama 2, and Gemini) can perform a wide range of tasks at a level comparable to or slightly better than an untrained human, none of these models currently outperform the median of skilled adults. Moreover, these models lack the ability to independently acquire new skills, and their capabilities remain largely confined to natural language processing.
An Artificial Superintelligence (ASI)—an AI that surpasses 100% of humans—is not currently in sight.
💻Book Software Demo
Experience the power of d.velop’s software with a personalised live demo, easily requested with just a few clicks. Watch as the software comes to life before your eyes and ask any questions you may have in real-time.
Developments and Trends in Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence continues to evolve and is expected to play an even more central role in the world of technology and business in the future. We’ve summarised some of the key trends identified by the market research and analysis firm Gartner:
Further Improvement of Generative AI Models: The rapid and widespread adoption of generative AI models is driving further innovation. New models will emerge that can generate content with increasingly higher quality.
Innovations “fueled by Generative AI”: Generative AI models—especially large language models and tools like Stable Diffusion—are gaining popularity. Software providers are actively experimenting with these technologies, and the integration of generative AI into existing applications is expected to grow significantly.
Edge AI: Gartner predicts a rise in demand for Edge AI, which refers to running AI models directly on end-user devices. This can help organisations gain real-time insights while meeting strict data protection requirements. For example, Google recently released MobileDiffusion, a model capable of performing text-to-image generation directly on smartphones.
Responsible AI: The field of Responsible AI focuses on the ethical, legal, and social implications of artificial intelligence, promoting its responsible and fair use.
Open Source Generative AI: In early 2023, Meta released LLaMA, the first open-source model of its kind. Open-source models—whose parameters are freely accessible—contribute to the democratisation of this disruptive technology. Making such models widely available could significantly accelerate progress in their development.
These trend forecasts from Gartner highlight that artificial intelligence will play an increasingly important role in the future of technology and business. The various types of AI offer immense opportunities for organisations, companies, and individuals. It is already clear that AI will soon transform the way we work, live, and interact.
